Gracechurch Street
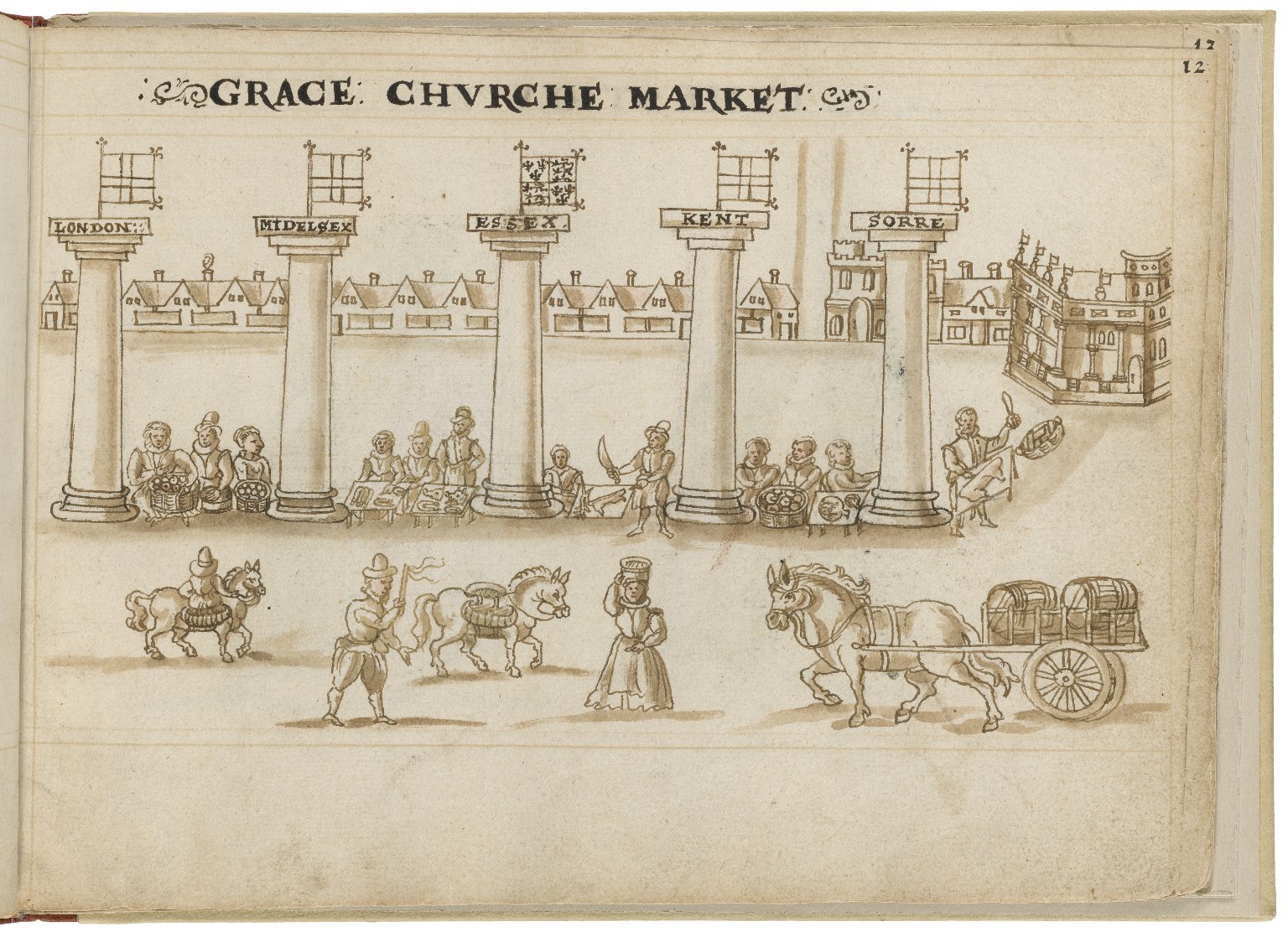
Gracechurch or Gracious
Street was a late Anglo-Saxon street. It seems to have been built
around the same time as London Bridge (tenth or
eleventh century), to which it provided access.
Gracechurch Street ran north-south from Cornhill Street near Leadenhall Market to the bridge. At the southern end, it was called
New Fish Street.North of Cornhill, Gracechurch continued as Bishopsgate Street, leading through Bishop’s Gate out of the walled city into the suburb of Shoreditch.
When the Burbage brothers (Richard and Cuthbert) dismantled the Theatre at Christmas 1598 in order to rebuild it as the
Globe in Southwark, it is very likely
that they brought the timbers on carts from Shoreditch down Bishopsgate Street,
Gracechurch Street, and New Fish Street, and thence across the Thames to
their new property on the south bank of the Thames just west of the bridge.
Gracechurch Street was on the royal processional route. When a king or queen
entered the City from the Tower, he or she stopped
in Gracechurch Street to witness the first of a
series of pageants prepared by London to welcome the new monarch.
See also: Chalfant 88.
References
-
Citation
Chalfant, Fran C. Ben Jonson’s London: A Jacobean Placename Dictionary. Athens: U of Georgia P, 1978.This item is cited in the following documents:
Cite this page
MLA citation
.
Gracechurch Street.The Map of Early Modern London, edited by , U of Victoria, 20 Jun. 2018, mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm.
Chicago citation
.
Gracechurch Street.The Map of Early Modern London. Ed. . Victoria: University of Victoria. Accessed June 20, 2018. http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm.
APA citation
2018. Gracechurch Street. In (Ed), The Map of Early Modern London. Victoria: University of Victoria. Retrieved from http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm.
RIS file (for RefMan, EndNote etc.)
Provider: University of Victoria Database: The Map of Early Modern London Content: text/plain; charset="utf-8" TY - ELEC A1 - Jenstad, Janelle ED - Jenstad, Janelle T1 - Gracechurch Street T2 - The Map of Early Modern London PY - 2018 DA - 2018/06/20 CY - Victoria PB - University of Victoria LA - English UR - http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm UR - http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/xml/standalone/GRAC1.xml ER -
RefWorks
RT Web Page SR Electronic(1) A1 Jenstad, Janelle A6 Jenstad, Janelle T1 Gracechurch Street T2 The Map of Early Modern London WP 2018 FD 2018/06/20 RD 2018/06/20 PP Victoria PB University of Victoria LA English OL English LK http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm
TEI citation
<bibl type="mla"><author><name ref="#JENS1"><surname>Jenstad</surname>, <forename>Janelle</forename></name></author>. <title level="a">Gracechurch Street</title>. <title level="m">The Map of Early Modern London</title>, edited by <editor><name ref="#JENS1"><forename>Janelle</forename> <surname>Jenstad</surname></name></editor>, <publisher>U of Victoria</publisher>, <date when="2018-06-20">20 Jun. 2018</date>, <ref target="http://mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm">mapoflondon.uvic.ca/GRAC1.htm</ref>.</bibl>Personography
-
Janelle Jenstad
JJ
Janelle Jenstad, associate professor in the department of English at the University of Victoria, is the general editor and coordinator of The Map of Early Modern London. She is also the assistant coordinating editor of Internet Shakespeare Editions. She has taught at Queen’s University, the Summer Academy at the Stratford Festival, the University of Windsor, and the University of Victoria. Her articles have appeared in the Journal of Medieval and Early Modern Studies, Early Modern Literary Studies, Elizabethan Theatre, Shakespeare Bulletin: A Journal of Performance Criticism, and The Silver Society Journal. Her book chapters have appeared (or will appear) in Performing Maternity in Early Modern England (Ashgate, 2007), Approaches to Teaching Othello (Modern Language Association, 2005), Shakespeare, Language and the Stage, The Fifth Wall: Approaches to Shakespeare from Criticism, Performance and Theatre Studies (Arden/Thomson Learning, 2005), Institutional Culture in Early Modern Society (Brill, 2004), New Directions in the Geohumanities: Art, Text, and History at the Edge of Place (Routledge, 2011), and Teaching Early Modern English Literature from the Archives (MLA, forthcoming). She is currently working on an edition of The Merchant of Venice for ISE and Broadview P. She lectures regularly on London studies, digital humanities, and on Shakespeare in performance.Roles played in the project
-
Author
-
Author of Abstract
-
Author of Stub
-
Author of Term Descriptions
-
Author of Textual Introduction
-
Compiler
-
Conceptor
-
Copy Editor
-
Course Instructor
-
Course Supervisor
-
Course supervisor
-
Data Manager
-
Editor
-
Encoder
-
Encoder (Structure and Toponyms)
-
Final Markup Editor
-
GIS Specialist
-
Geographic Information Specialist
-
Geographic Information Specialist (Modern)
-
Geographical Information Specialist
-
JCURA Co-Supervisor
-
Main Transcriber
-
Markup Editor
-
Metadata Co-Architect
-
MoEML Transcriber
-
Name Encoder
-
Peer Reviewer
-
Primary Author
-
Project Director
-
Proofreader
-
Researcher
-
Reviser
-
Second Author
-
Second Encoder
-
Toponymist
-
Transcriber
-
Transcription Proofreader
-
Vetter
Contributions by this author
Janelle Jenstad is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Janelle Jenstad is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Tye Landels-Gruenewald
TLG
Research assistant, 2013-15, and data manager, 2015 to present. Tye completed his undergraduate honours degree in English at the University of Victoria in 2015.Roles played in the project
-
Author
-
Author of Term Descriptions
-
CSS Editor
-
Compiler
-
Conceptor
-
Copy Editor
-
Data Manager
-
Editor
-
Encoder
-
Geographic Information Specialist
-
Markup Editor
-
Metadata Architect
-
MoEML Researcher
-
Name Encoder
-
Proofreader
-
Researcher
-
Toponymist
-
Transcriber
Contributions by this author
Tye Landels-Gruenewald is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Tye Landels-Gruenewald is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Kim McLean-Fiander
KMF
Director of Pedagogy and Outreach, 2015–present; Associate Project Director, 2015–present; Assistant Project Director, 2013-2014; MoEML Research Fellow, 2013. Kim McLean-Fiander comes to The Map of Early Modern London from the Cultures of Knowledge digital humanities project at the University of Oxford, where she was the editor of Early Modern Letters Online, an open-access union catalogue and editorial interface for correspondence from the sixteenth to eighteenth centuries. She is currently Co-Director of a sister project to EMLO called Women’s Early Modern Letters Online (WEMLO). In the past, she held an internship with the curator of manuscripts at the Folger Shakespeare Library, completed a doctorate at Oxford on paratext and early modern women writers, and worked a number of years for the Bodleian Libraries and as a freelance editor. She has a passion for rare books and manuscripts as social and material artifacts, and is interested in the development of digital resources that will improve access to these materials while ensuring their ongoing preservation and conservation. An avid traveler, Kim has always loved both London and maps, and so is particularly delighted to be able to bring her early modern scholarly expertise to bear on the MoEML project.Roles played in the project
-
Associate Project Director
-
Author
-
Author of MoEML Introduction
-
CSS Editor
-
Compiler
-
Contributor
-
Copy Editor
-
Data Contributor
-
Data Manager
-
Director of Pedagogy and Outreach
-
Editor
-
Encoder
-
Encoder (People)
-
Geographic Information Specialist
-
JCURA Co-Supervisor
-
Managing Editor
-
Markup Editor
-
Metadata Architect
-
Metadata Co-Architect
-
MoEML Research Fellow
-
MoEML Transcriber
-
Proofreader
-
Researcher
-
Second Author
-
Secondary Author
-
Secondary Editor
-
Toponymist
-
Vetter
Contributions by this author
Kim McLean-Fiander is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Kim McLean-Fiander is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Joey Takeda
JT
Programmer, 2018-present; Junior Programmer, 2015 to 2017; Research Assistant, 2014 to 2017. Joey Takeda is an MA student at the University of British Columbia in the Department of English (Science and Technology research stream). He completed his BA honours in English (with a minor in Women’s Studies) at the University of Victoria in 2016. His primary research interests include diasporic and indigenous Canadian and American literature, critical theory, cultural studies, and the digital humanities.Roles played in the project
-
Author
-
Author of Abstract
-
Author of Stub
-
CSS Editor
-
Compiler
-
Conceptor
-
Copy Editor
-
Data Manager
-
Date Encoder
-
Editor
-
Encoder
-
Encoder (Bibliography)
-
Geographic Information Specialist
-
Geographic Information Specialist (Agas)
-
Junior Programmer
-
Markup Editor
-
Metadata Co-Architect
-
MoEML Encoder
-
MoEML Transcriber
-
Programmer
-
Proofreader
-
Researcher
-
Second Author
-
Toponymist
-
Transcriber
-
Transcription Editor
Contributions by this author
Joey Takeda is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Joey Takeda is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Stewart Arneil
Programmer at the University of Victoria Humanities Computing and Media Centre (HCMC) who maintained the Map of London project between 2006 and 2011. Stewart was a co-applicant on the SSHRC Insight Grant for 2012–16.Roles played in the project
-
Programmer
Stewart Arneil is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Stewart Arneil is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Martin D. Holmes
MDH
Programmer at the University of Victoria Humanities Computing and Media Centre (HCMC). Martin ported the MOL project from its original PHP incarnation to a pure eXist database implementation in the fall of 2011. Since then, he has been lead programmer on the project and has also been responsible for maintaining the project schemas. He was a co-applicant on MoEML’s 2012 SSHRC Insight Grant.Roles played in the project
-
Author
-
Author of abstract
-
Conceptor
-
Encoder
-
Name Encoder
-
Post-conversion and Markup Editor
-
Programmer
-
Proofreader
-
Researcher
Contributions by this author
Martin D. Holmes is a member of the following organizations and/or groups:
Martin D. Holmes is mentioned in the following documents:
-
-
Hugh Alley
Freeman of the City of London, whistle-blower, and author of A Caveatt for the Citty of London.Hugh Alley is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Richard Burbage
(b. 1568, d. 1619)Actor with the Lord Chamberlain’s Men (later the King’s Men) and younger son of James Burbage.Richard Burbage is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Cuthbert Burbage
(b. between 1564 and 1565, d. 1636)Actor, theatre entrepreneur, son of James Burbage, and elder brother of Richard Burbage.Cuthbert Burbage is mentioned in the following documents:
Locations
-
Cornhill
Cornhill was a significant thoroughfare and was part of the cityʼs main major east-west thoroughfare that divided the northern half of London from the southern half. The part of this thoroughfare named Cornhill extended from St. Andrew Undershaft to the three-way intersection of Threadneedle, Poultry, and Cornhill where the Royal Exchange was built. The nameCornhill
preserves a memory both of the cornmarket that took place in this street, and of the topography of the site upon which the Roman city of Londinium was built.Cornhill is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Leadenhall is mentioned in the following documents:
-
New Fish Street
New Fish Street (also known in the seventeenth century as Bridge Street) ran north-south from London Bridge at the south to the intersection of Eastcheap, Gracechurch Street, and Little Eastcheap in the north (Harben; BHO). At the time, it was the main thoroughfare to London Bridge (Sugden 191). It ran on the boundary between Bridge Within Ward on the west and Billingsgate Ward on the east. It is labelled on the Agas map asNew Fyshe streate.
Variant spellings includeStreet of London Bridge,
Brigestret,
Brugestret,
andNewfishstrete
(Harben; BHO).New Fish Street is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Bishopsgate Street
Bishopsgate Street ran north from Cornhill Street to the southern end of Shoreditch Street at the city boundary. South of Cornhill, the road became Gracechurch Street, and the two streets formed a major north-south artery in the eastern end of the walled city of London, from London Bridge to ShoreditchImportant sites included: Bethlehem Hospital, commonly corrupted to the short form -bedlam, a mental hospital and Bull Inn, where plays were performedbefore Shakespeare’s time
(Weinreb and Hibbert 67).Bishopsgate Street is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Bishopsgate is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Shoreditch is mentioned in the following documents:
-
London Bridge
From the time the first wooden bridge in London was built by the Romans in 52 CE until 1729 when Putney Bridge opened, London Bridge was the only bridge across the Thames in London. During this time, several structures were built upon the bridge, though many were either dismantled or fell apart. John Stow’s 1598 A Survey of London claims that the contemporary version of the bridge was already outdated by 994, likely due to the bridge’s wooden construction (Stow 1:21).London Bridge is mentioned in the following documents:
-
The Globe is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Southwark is mentioned in the following documents:
-
Tower of London is mentioned in the following documents:
Variant spellings
-
Documents using the spelling
Garscherch street
-
Documents using the spelling
Grace Church
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracechurch
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracechurch street
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracechurch Street
-
Documents using the spelling
gracious
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious Street
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious street
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious streete
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious-street
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious-street
-
Documents using the spelling
Gracious-streete
-
Documents using the spelling
Graschestret
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse church
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse Church
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse church streete
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse street
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse Street
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse streete
-
Documents using the spelling
Grasse stréete
-
Documents using the spelling
Grassestreete
-
Documents using the spelling
Grastreet
-
Documents using the spelling
Grastreete
-
Documents using the spelling
Gratious Street

